This month we explore academic publications on the topics of developing a numerical surface-water/groundwater model for the lower San Antonio River Basin, using a geophysical technique—a gradient self-potential logging survey—to assess surface water-groundwater interaction on the Rio Grande in the Mesilla Valley, and utilizing a 20-member climate model to learn how a warmer climate could impact future droughts.
Sections
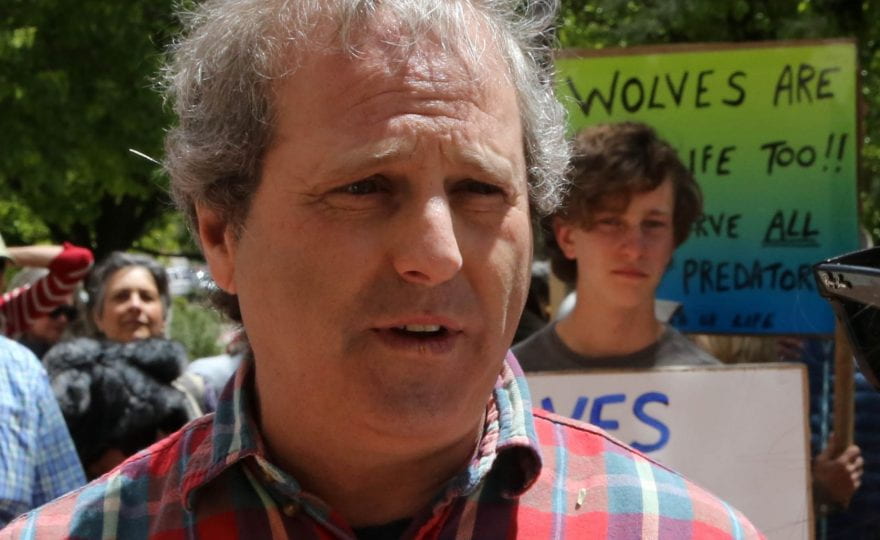
q&a+water: Michael Robinson
In this issue’s Q&A, Texas+Water Editor-in-Chief, Dr. Todd Votteler, interviews Michael Robinson, Senior Conservation Advocate for the Center for Biological Diversity.
The State of Texas Water Infrastructure
Earlier this month, during a special session of the Texas Legislature, the Texas Capitol flooded. After the water stopped cascading down the pink granite walls inside the Capitol extension, the Legislature resumed its deliberations. The August flood was preceded by February’s Winter Storm Uri. Between 200 and 700 Texans died in the cold and dark after days without power and, in some places, without water. According to the Electric Reliability Council of Texas, the electric
think+water: Climate Change Education in DFW, Mussels and the 2011 Drought, and Sampling Springs in the Edwards Aquifer System
This month we explore academic publications on the topics of barriers and opportunities for climate change education in Texas, understanding the impacts of drought on mussels in the Colorado River Basin, and tracing the origin of water and hydrological processes in the Edwards Aquifer system.
opinions+water: Texas Water Utilities Provide a Snapshot of Financial Conditions and Prospects for Addressing Texas Water Infrastructure Needs in 2021 and 2022
Recently, Water Opinions LLC teamed up with the Texas Water Infrastructure Network for the second annual assessment of current and future Texas water infrastructure projects, financing and other issues facing Texas water utilities.